Low Noise Multi specification Integrated-Structure Planetary Reducer AHS Series
Cat:Planetary Reducer
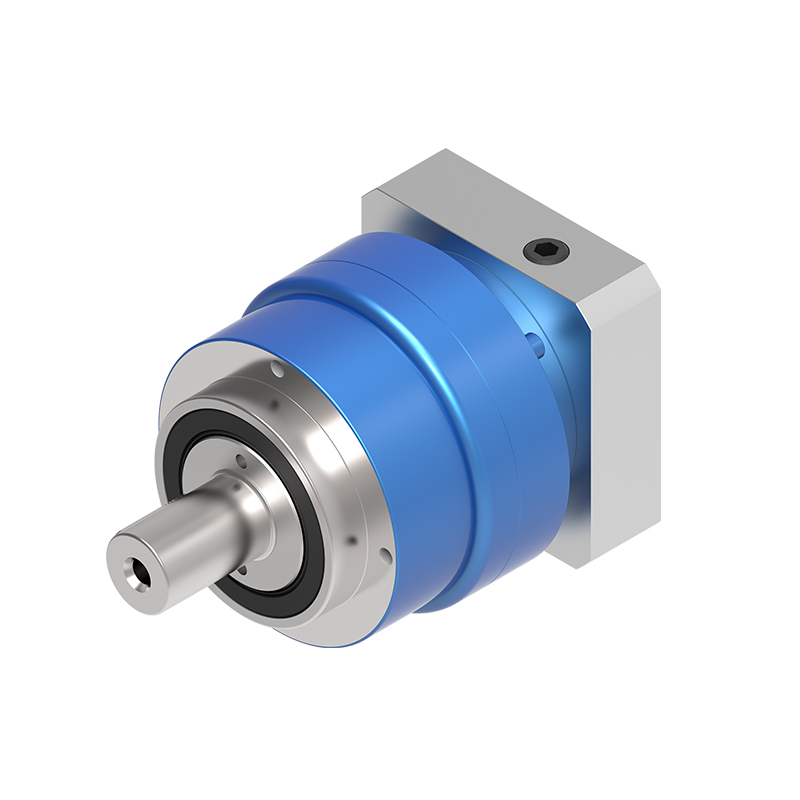
Planetary reducers occupy an important position in the field of industrial automation. The high-prec...
See DetailsIn the world of industrial automation and precision motion control, the choice of a power transmission component can define the success of an application. Among these, the planetary reducer stands out for its compact design, high efficiency, and exceptional torque density. This comprehensive guide delves into the technology behind planetary gearboxes, explores key selection criteria, and examines their vital role across various industries.
A planetary reducer, also known as a planetary gearbox, is a compact, high-torque transmission system. Its name derives from its gear arrangement, which resembles a solar system. A central "sun" gear is driven by the input motor, which in turn drives multiple "planet" gears orbiting around it. These planet gears are held within a rotating carrier and mesh with an outer ring gear. This ingenious design distributes the load across multiple contact points, leading to its superior characteristics.
When compared to alternative gear systems like spur or worm gearboxes, planetary reducers offer distinct benefits. These advantages are crucial for demanding applications in robotics, aerospace, and advanced manufacturing.
To make an informed choice, it's essential to understand how planetary reducers stack up against other common types. The following analysis highlights key performance differences.
| Feature | Planetary Reducer | Worm Gear Reducer | Spur Gear Reducer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Very High (≥97%) | Low to Moderate (50-90%) | High (94-98%) |
| Torque Density | Excellent | Good | Low |
| Backlash | Can be very low | Typically higher | Moderate |
| Compactness | Excellent (coaxial) | Moderate | Poor (offset shafts) |
| Cost for High Performance | Higher | Lower | Moderate |
This comparison clearly shows that for applications demanding compact size, high efficiency, and precision, the planetary design is often unrivaled[1].
Selecting the optimal planetary reducer is critical for system performance and longevity. Engineers must consider several interconnected parameters.
Specific application needs often lead to focused searches. For instance, a designer working on a new robotic joint will prioritize compactness and precision, leading them to search for solutions like a compact planetary gearbox for robotics. Similarly, applications involving frequent start-stop cycles or high inertial loads necessitate a unit with high overhung load capacity, which is a key feature in a high torque planetary reducer with low backlash. Understanding these nuanced needs is part of the selection process.
The exceptional performance of a premium planetary reducer is not accidental; it is the result of meticulous design, advanced manufacturing, and rigorous quality control. The process begins with precision gear hobbing and grinding to ensure perfect tooth profiles. Heat treatment, such as carburizing, is then applied to achieve the ideal balance of a hard, wear-resistant surface and a tough, shock-absorbing core. Final assembly in a controlled environment, followed by comprehensive testing for noise, vibration, efficiency, and backlash, guarantees the unit meets its specifications. This dedication to process is what allows a reducer to deliver reliable, long-term performance in critical applications.
The unique blend of power, precision, and compactness makes planetary gearboxes indispensable in modern industry.
In sectors like packaging machinery, where smooth, continuous operation is vital, the demand for a planetary gearbox for packaging machinery is high due to its ability to handle variable loads with minimal vibration. For engineers integrating a servo motor, finding the perfect match is key, which is why understanding the interface and performance synergy of a servo motor planetary reducer is a common focus area. Furthermore, mobile applications in agriculture or construction often require a planetary gear drive for mobile equipment that can withstand shock loads and harsh environments while delivering high power density.
Proper care extends the operational life of a planetary reducer significantly.
For maintenance teams, specific symptoms point to particular problems. A sudden increase in operating temperature often indicates lubrication issues or overloading. Excessive backlash or positioning error can stem from gear wear or bearing failure. Identifying the root cause of such issues is a skill honed over time and is critical for preventing downtime.
The evolution of planetary reducers is closely tied to advancements in adjacent fields. The rise of collaborative robots (cobots) and exoskeletons demands even more compact, lightweight, and backdrivable units. Integration with direct-drive technologies and smart sensors for predictive maintenance (Industry 4.0) is becoming more prevalent. Furthermore, the development of new materials, such as advanced composites and high-performance polymers, promises to reduce weight and inertia further. Manufacturers at the forefront, such as BEITTO, which adheres to meticulous Japanese R&D and production philosophies, are continuously researching these areas from strategic locations like the National (Jiaxing) Electromechanical Components Industrial Park in Pinghu—a hub within China's dynamic Yangtze River Delta region—to achieve ongoing optimization and structural upgrades in planetary reducer design[2].
The primary advantage is its superior torque density and compact coaxial design. It delivers more torque in a smaller, more rigid package compared to many other gearbox types, making it ideal for space-constrained, high-performance applications.
The reduction ratio is calculated based on your motor's speed and torque characteristics and your load's required output speed and torque. A key formula is: Required Output Torque = Motor Torque x Reduction Ratio x Efficiency. You must also ensure the motor can provide sufficient power to accelerate the load inertia reflected through the ratio.
Yes, many planetary reducers are designed for universal mounting. However, it is crucial to consult the manufacturer's specifications. Vertical mounting can affect lubrication distribution and bearing loads, so specific models or lubrication plans may be recommended for such orientations.
Backlash is the slight angular movement between the input and output shafts when direction is reversed, with the output held stationary. Low backlash is critical for applications requiring high positioning accuracy and repeatability, such as in robotics or CNC machinery, as it minimizes "play" or error in the system.
Lubrication intervals depend entirely on the operating conditions, speed, temperature, and reducer model. Some are filled with lifelong lubricant, while others require periodic changes. Always use the lubricant type (grease or oil) and viscosity grade specified by the manufacturer to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
[1] Dudley, D. W., & Winter, H. (1984). *Gear Handbook: The Design, Manufacture, and Application of Gears*. McGraw-Hill. (Reference for general gearbox efficiency and performance comparisons).
[2] Information on Pinghu City and the National Electromechanical Components Industrial Park sourced from the official economic development and zoning documentation of Pinghu Municipal Government, Zhejiang Province. (Provides contextual background on the industrial region mentioned).